Within the last decade, a new link between spirituality and neuroscience has emerged in scientific and spiritual fields. Recent data shows the immense effect of faith, belief, and dedication on the brain’s growth. This article will explore all the evidence and share some transformative techniques to demonstrate the importance of positive/meaningful thinking in shaping a healthy brain.
The Power of Neuroplasticity:
Contrary to what most people assume, our brains can continuously rewrite themselves
based on our activities and experiences outside the inner realm.
Neuroplasticity plays an essential role in linking spirituality with neuroscience. It is the brain’s
capacity to adapt and change in response to new practices and environmental shifts. Spiritual activities s
uch as meditation, prayer, and breathwork have been globally acknowledged to induce measurable changes in the brain.
Studies using neuroimaging techniques such as fMRI and EEG have found that regular meditation leads to changes
in brain regions associated with attention, emotional regulation, and self-awareness. Those who regularly engage
in meditation have been observed to have increased grey matter density in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus,
which are regions linked to cognitive control and memory.
The beauty all spiritual activities share is that they induce a sense of ascendence and awareness boost, both are
critical in stimulating certain parts of the brain or help reduce activities in other areas. The DMN, which stands
for default mode network, is a huge-scale brain network activated when we are not focused on external activities;
It is mainly associated with inner observation, mind wandering and self-refining. Upon practising spiritual activities,
modulation of the DMN occurs, leading to a sense of oneness and an optimised state of being.
Another area of the brain is called The Salience Network. It is mainly responsible for detecting and prioritising
objects and information in the surrounding environmen. During Mindfulness, the brain experiences reduced activities
in regions like the Medial thalamus and caudate, both associated with sensory and emotional processing, leading to a
shift in attention towards what to prioritise externally and promoting a feeling of being something greater than oneself.
Emotional And Mental Wellbeing:

It's no stranger that the role of spirituality and religion is helping millions worldwide
find peace and meaning in their lives, making it a solid source of solace and resilience,
especially in challenging times.
We are blessed with consciousness and are evaluated as spiritual entities, to the beauty of observing the world
via emotions and thoughts. However, this is no easy task. When the human psyche experiences intense pressure
from external sources, it appears its true form of identity, and it is required to react. Belief plays a
crucial role here; surrendering to our purest forms during challenging times is what makes us humans; it's
also the situation where many people of all ages are known to make miracles. To change not only their lives but also those of others.
A true Fact is that people who engage in spiritual activities are known to react less to stress or anxiety,
are more encouraging, and are naturally courageous. In addition to having a solid immunity against depression,
they are more resilient when it comes to coping with traumatic events. All of this is achieved through surrendering and pure belief.
The Brain Before and After Meditation: Scientific Materials
The following are real brain scans performed by legit experts in their fields; more information about each experiment will be linked.
1. Binghamton University Study:
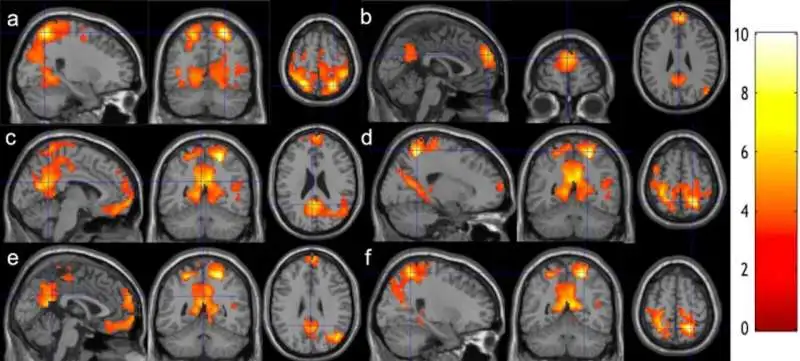
Researchers conducted a study scanning some of their students' brains before and after eight weeks of practising
meditation under a professional trainer. This study emphasises how just two months into meditation can show intriguing
results.
These MRI scans revealed significant changes in some brain patterns, explaining the impact of meditation on cognition and overall neural
activity. This research knew light thanks to a casual chat between Assistant Professor Weijying Dai and Lecturer Gorge Weinschenk. Both
are experts
in longtime meditation, brain mapping and biochemical image processing, more details can be found Within The official study Publication. Sources: Research shows just 8 weeks of meditation studies can make your brain quicker
2. Noobs vs Experts in Meditation: University of Wisconsin and its affiliates study
This study focused on learning about what makes long-term meditators vs novices. What makes the difference within
their brains? And How it reflected in their lives.
Functional resonance imaging (fMRI) revealed distinct patterns in emotions-related brain networks, showing
that long-term meditators dedicated to mindfulness and meditation experiences exhibited unique neural connectivity.
Sources: Meditation affects brain networks differently in long-term meditators and novices -Impact of short- and long-term mindfulness meditation training on amygdala reactivity to emotional stimuli
Mindfulness meditation improves connections in the brain: Harvard medication school.
Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital used MRI scans to observe changes in gray matter associated with mindfulness meditation.
Gray matter refers to the parts of the brain that contain cell bodies and synapses, and it plays a crucial
role in processing information and regulating emotions.
The findings of this study add to a growing body of research supporting the idea that meditation can induce neuroplasticity,
the brain's ability to reorganise and form new connections in response to experience.
Researchers hope to better understand how mindfulness meditation exerts its effects and how it might be
used as a therapeutic intervention for various mental health conditions. Mindfulness meditation improves connections in the brain




